It's not just the isolation. Working from home has surprising downsides
- Written by Libby Sander, Assistant Professor of Organisational Behaviour, Bond Business School, Bond University
What if you never had to return to work? Never had to return to work at the office, that is.
You’d be able to juggle kids on school holidays. You wouldn’t need to navigate traffic jams. Your employer might gain increased productivity, lower turnover and lower lease costs. But there are less obvious downsides.
In 2010, as part of building a case for the national broadband network, the Gillard government set a target for teleworking, suggesting the Australian economy could save between A$1.4 billion and A$1.9 billion a year if 10% of the workforce teleworked half the time.
Her successors have cooled on the idea. The web address www.telework.gov.au no longer works and reliable statistics for telework don’t exist.
Yet it’s attractive.
It seems like a grand idea…
Studies find working from home cuts commuting times and associated fatigue, transport congestion, and environmental impacts. Worldwide, an increasing number of employers are allowing it in order to attract and retain staff.
Employees value it as a way to maintain a work-life balance, in particular millennials.
And the office has become a nightmare for some. A tide of research finds many employees working in modern open-plan offices are so distracted by noise and interruptions they can’t concentrate.
Read more: A new study should be the final nail for open-plan offices
In my research on the workplace, employees frequently tell me they have to work from home to get work done.
Other research supports these findings. A two-year study using randomly assigned groups found a 13% productivity increase. It also found turnover decreased by 50% among those working at home and that they took shorter breaks and fewer sick days. And the company saved around US$2,000 (A$2,784) per employee on lease costs.
It’s enough to make employers allow working from home for everyone who can. But a key finding from the same study sounds a cautionary note.
More than half the volunteers that worked from home felt so isolated they changed their minds about wanting to do it all the time.
…until you try it
It’s not just isolation and loneliness.
Research shows working from home is far worse for team cohesion and innovation than working in the office.
In 2013 Yahoo chief executive Marissa Meyer banned working from home, saying that in order “to become the absolute best place to work, communication and collaboration will be important, so we need to be working side-by-side. That is why it is critical that we are all present in our offices.”
Since then, other large corporates including Bank of America and IBM have followed suit.
Read more: Marissa Mayer is right: your company needs you (in the office)
Contrary to what we might think, research shows that as the availability of laptops and other remote work devices increases, proximity has becoming more important.
One study showed that engineers who shared a physical office were 20% more likely to stay in touch digitally than those who worked remotely. Employees who were in the same office emailed four times as often to collaborate on shared projects than staff who weren’t in the office. The result, for these sorts of projects, was 32% faster project completion times.
Other research finds face to face interaction is essential for identifying opportunities for collaboration, innovation and developing relationships and networks.
Another study of home workers from 15 countries found 42% of remote workers had trouble sleeping, waking up repeatedly in the night, compared to only 29% who always worked in the office.
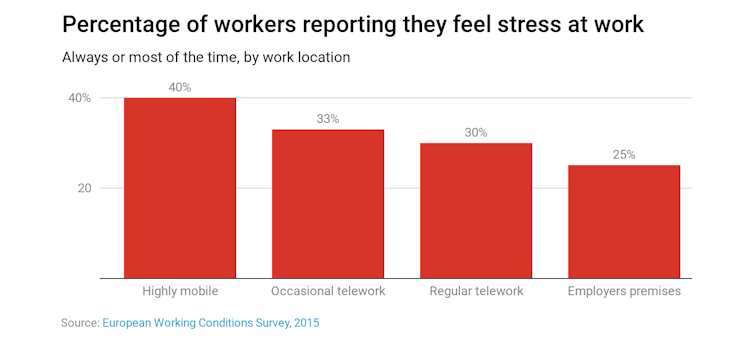
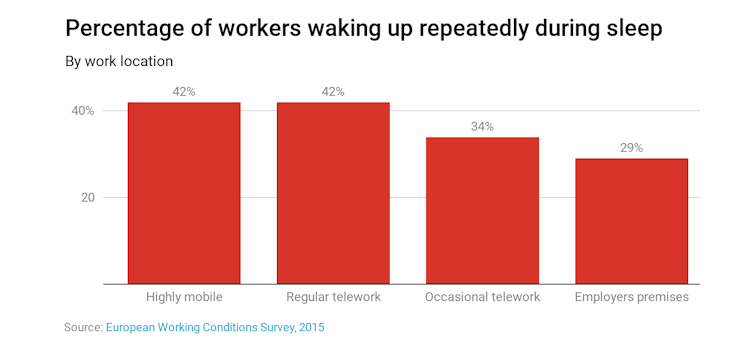 Some 41% of highly mobile workers felt stress “always or most of the time” compared to only 25% who always worked at the office.
Part of the stress is due to being tethered to mobile devices, often kept by beds, as well as the challenges of working from home. Locating colleagues to keep projects moving and trying to do conference calls surrounded by children, barking dogs or delivery people at the door is not as easy as it sounds.
Some 41% of highly mobile workers felt stress “always or most of the time” compared to only 25% who always worked at the office.
Part of the stress is due to being tethered to mobile devices, often kept by beds, as well as the challenges of working from home. Locating colleagues to keep projects moving and trying to do conference calls surrounded by children, barking dogs or delivery people at the door is not as easy as it sounds.
 Perhaps not surprisingly then, another study finds that, rather than being helpful, working from home is likely to interfere with family life.
And other studies suggest not being in the office regularly can hinder your career, resulting in being overlooked for projects or promotions. Out of sight can mean out of mind.
For some, what’s best will be some of both
There are strong, evidence-based reasons to both work from home and the office. So, what’s best?
One thing that can be said with certainty is that workers shouldn’t be forced to work from home because the office is too noisy for them to concentrate.
Employers need to ensure the workplace is designed effectively for the type of work that needs to be done, and also for the type of people who work there.
Access to flexible work, including working from home is important, but it needs to be balanced with the benefits of face to face interaction.
Read more:
The rise of the coworking space – sign of the times or flash in the pan?
A halfway house is for employees working from home to have access to shared coworking spaces (working with workers from other firms and other industries) where they can get some of the benefits of being in the office without having to travel there.
Coworking spaces have been shown to reduce isolation, while providing employees with the benefits of access to a more diverse network and exposure to innovative ideas.
Read more:
The benefits – and pitfalls – of working in isolation
Perhaps not surprisingly then, another study finds that, rather than being helpful, working from home is likely to interfere with family life.
And other studies suggest not being in the office regularly can hinder your career, resulting in being overlooked for projects or promotions. Out of sight can mean out of mind.
For some, what’s best will be some of both
There are strong, evidence-based reasons to both work from home and the office. So, what’s best?
One thing that can be said with certainty is that workers shouldn’t be forced to work from home because the office is too noisy for them to concentrate.
Employers need to ensure the workplace is designed effectively for the type of work that needs to be done, and also for the type of people who work there.
Access to flexible work, including working from home is important, but it needs to be balanced with the benefits of face to face interaction.
Read more:
The rise of the coworking space – sign of the times or flash in the pan?
A halfway house is for employees working from home to have access to shared coworking spaces (working with workers from other firms and other industries) where they can get some of the benefits of being in the office without having to travel there.
Coworking spaces have been shown to reduce isolation, while providing employees with the benefits of access to a more diverse network and exposure to innovative ideas.
Read more:
The benefits – and pitfalls – of working in isolation
Authors: Libby Sander, Assistant Professor of Organisational Behaviour, Bond Business School, Bond University





