Vital Signs: the best thing for jobs now is to accelerate the vaccine roll-out
- Written by Richard Holden, Professor of Economics, UNSW
Australia has navigated the COVID-19 pandemic and is now in better economic shape than most countries due to a two-pronged strategy.
First, we quickly got the virus largely under control – reflecting the reality it would have been impossible to have a properly functioning economy in the face of an out-of-control epidemic. Second, we had key economic support measures, most notably JobKeeper and JobSeeker.
But with those measures ending, and Australia’s vaccination rollout only just beginning – and proceeding at half the pace of the US, UK and other European nations – the economy is still nine to 12 months from being able to truly open up.
Many sectors stuck in 2020 mode
JobKeeper and JobSeeker were always designed to be transitory measures – a way to weather the crisis. Rather than ending these measures abruptly, the federal government wisely tapered them.
Reasonable minds can differ about the timing and the extent of that taper. I (and others) have criticised the federal government for doing so too quickly. It is unwise to cut back fiscal support prematurely when accommodative monetary policy – through 0.1% short-term and three-year interest rates – is doing all the work it can.
But the economy is still far from fully recovered. As we wait to achieve widespread vaccination, sectors such as hospitality, tourism, higher education and many more are stuck in 2020 mode. Restaurants and other venues are operating at reduced capacity. Domestic tourism remains dramatically reduced from pre-pandemic levels. International students cannot return to Australia while our international borders are (rightly) closed. The list goes on.
Will unemployment spike?
Next week, with the end of JobKeeper, a new phase of the fiscal-tapering experiment begins.
Economic output is still below what it was pre-pandemic. The unemployment rate has fallen (from its peak of 7.5% last July) to 5.8%, better than some expected but still way more than the 3.5%-4.0% likely required to achieve “full employment” and get wages growing again.
Australia’s unemployment rate
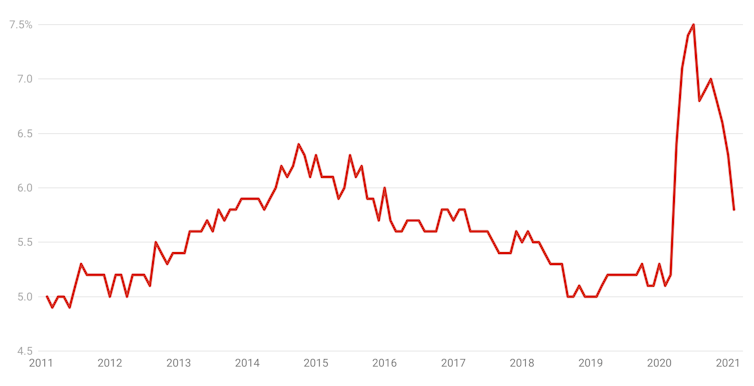 ABS labour force statistics, February 2021, CC BY-NC
The big unknown is how much unemployment will spike with JobKeeper’s end. How many businesses are still relying on those wage subsidies to keep people employed?
Treasury boss Steven Kennedy told a Senate Estimates hearing this week that 100,000 to 150,000 jobs may be lost.
Steven Kennedy at Senate Estimates.That is broadly consistent with estimates from the Commonwealth Bank, which reckons the loss will be about 110,000 jobs, and of Australia’s leading labour economist, Jeff Borland at the University of Melbourne, who has calculated it will be 125,000 to 250,000 jobs.
However, with 50,000 to 60,000 jobs a month having been added in recent times, Borland is also optimistic it may only take a few months to wipe out these losses.
Read more:
Vital Signs: we'll never cut unemployment to 0%, but less than 4% should be our goal
Stars must align
That may be right. We should certainly hope it is. But more than a few stars have to align for things to pan out that way.
The recent rate of jobs growth must continue, or speed up. It might do just that, but it’s unclear. The easiest jobs to replace tend to come back first. Jobs growth could well slow down because the lowest-hanging labour-market fruit have already been picked.
The movement of 150,000 or so people moving from employment to unemployment benefits will have a direct impact on spending in the economy. Although this may not be huge at the macroeconomic level, the spike in the unemployment rate could hurt consumer and business confidence. What if (to borrow a line from the prime minister) consumers and their wallets stay “under the doona”?
Vaccination roll-out now the key
The federal government won’t be reversing its decision to end JobKeeper. It may offer targeted support programs for certain sectors as a partial substitute but, if the half-price air-travel scheme is any indication of their quality and magnitude, they won’t have much effect.
Read more:
Marginal advantage: a whiff of pork in the government's great tourist ticket lottery
The best thing to do to get jobs growth up and the unemployment rate down is to accelerate the vaccine roll-out. Most Australians being vaccinated is the only way the economy will truly return to anything like that of December 2019.
That means importing more Pfizer, Moderna and Johnson & Johnson jabs, putting a fire under CSL’s domestic production of AstraZeneca, and establishing mass vaccination sites as other nations have done.
While we’re at it, Federal Health Minister Greg Hunt and health department head Brendan Murphy should stop saying “it’s not a race” and “we’re not in a hurry”, and show a greater sense of urgency.
ABS labour force statistics, February 2021, CC BY-NC
The big unknown is how much unemployment will spike with JobKeeper’s end. How many businesses are still relying on those wage subsidies to keep people employed?
Treasury boss Steven Kennedy told a Senate Estimates hearing this week that 100,000 to 150,000 jobs may be lost.
Steven Kennedy at Senate Estimates.That is broadly consistent with estimates from the Commonwealth Bank, which reckons the loss will be about 110,000 jobs, and of Australia’s leading labour economist, Jeff Borland at the University of Melbourne, who has calculated it will be 125,000 to 250,000 jobs.
However, with 50,000 to 60,000 jobs a month having been added in recent times, Borland is also optimistic it may only take a few months to wipe out these losses.
Read more:
Vital Signs: we'll never cut unemployment to 0%, but less than 4% should be our goal
Stars must align
That may be right. We should certainly hope it is. But more than a few stars have to align for things to pan out that way.
The recent rate of jobs growth must continue, or speed up. It might do just that, but it’s unclear. The easiest jobs to replace tend to come back first. Jobs growth could well slow down because the lowest-hanging labour-market fruit have already been picked.
The movement of 150,000 or so people moving from employment to unemployment benefits will have a direct impact on spending in the economy. Although this may not be huge at the macroeconomic level, the spike in the unemployment rate could hurt consumer and business confidence. What if (to borrow a line from the prime minister) consumers and their wallets stay “under the doona”?
Vaccination roll-out now the key
The federal government won’t be reversing its decision to end JobKeeper. It may offer targeted support programs for certain sectors as a partial substitute but, if the half-price air-travel scheme is any indication of their quality and magnitude, they won’t have much effect.
Read more:
Marginal advantage: a whiff of pork in the government's great tourist ticket lottery
The best thing to do to get jobs growth up and the unemployment rate down is to accelerate the vaccine roll-out. Most Australians being vaccinated is the only way the economy will truly return to anything like that of December 2019.
That means importing more Pfizer, Moderna and Johnson & Johnson jabs, putting a fire under CSL’s domestic production of AstraZeneca, and establishing mass vaccination sites as other nations have done.
While we’re at it, Federal Health Minister Greg Hunt and health department head Brendan Murphy should stop saying “it’s not a race” and “we’re not in a hurry”, and show a greater sense of urgency.
Authors: Richard Holden, Professor of Economics, UNSW





