It's bee season. To avoid getting stung, just stay calm and don't swat
- Written by Caitlyn Forster, PhD Candidate, School of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Sydney
This summer’s wetter conditions have created great conditions for flowering plants. Flowers provide sweet nectar and protein-rich pollen, attracting many insects, including bees.
Commercial honey bees are also thriving: the New South Wales population has reportedly bounced back after the drought and bushfires
While you may have seen a lot of bees around lately, there’s no reason to be afraid. Most bees are only aggressive when provoked, and some don’t sting at all. And some bee-like insects are actually flies.
We are experts on honey bee and other insect behaviour. So let’s look at which bees to watch out for, and how to avoid being stung this summer.
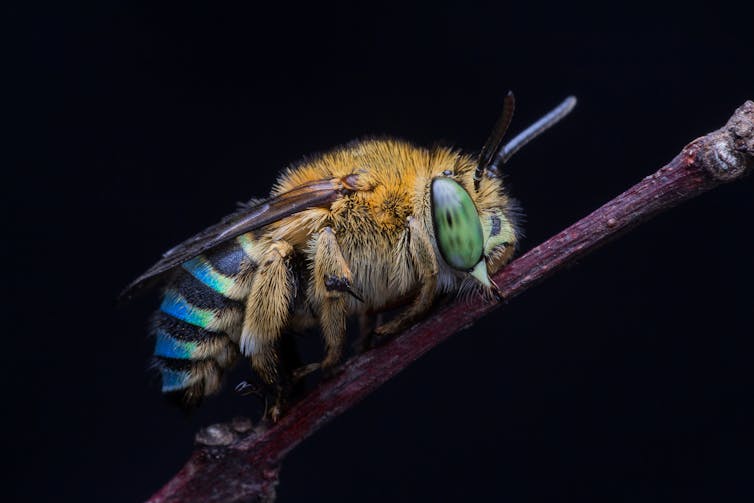 Most bees, like this native blue banded bee, are not very interested in people.
Shutterstock
Most bees, like this native blue banded bee, are not very interested in people.
Shutterstock
Is it a bee, or a wanna-bee?
Bees in Australia comprise both introduced and native species.
Invasive bees found in Australia, all of which can sting, include the widespread European honeybees, bumble bees in Tasmania, and Asian honey bees in Queensland.
Read more: The mystery of the blue flower: nature's rare colour owes its existence to bee vision
Australia is also home to about 2,000 native bees, including 11 stingless species.
Stingless bees live in colonies and produce honey. Other native species, such as blue banded bees and leaf cutter bees, are capable of stinging but are rarely aggressive.
Some insects we see around flowers are actually harmless hoverflies. But their yellow and black stripes mean they are often mistaken for bees.
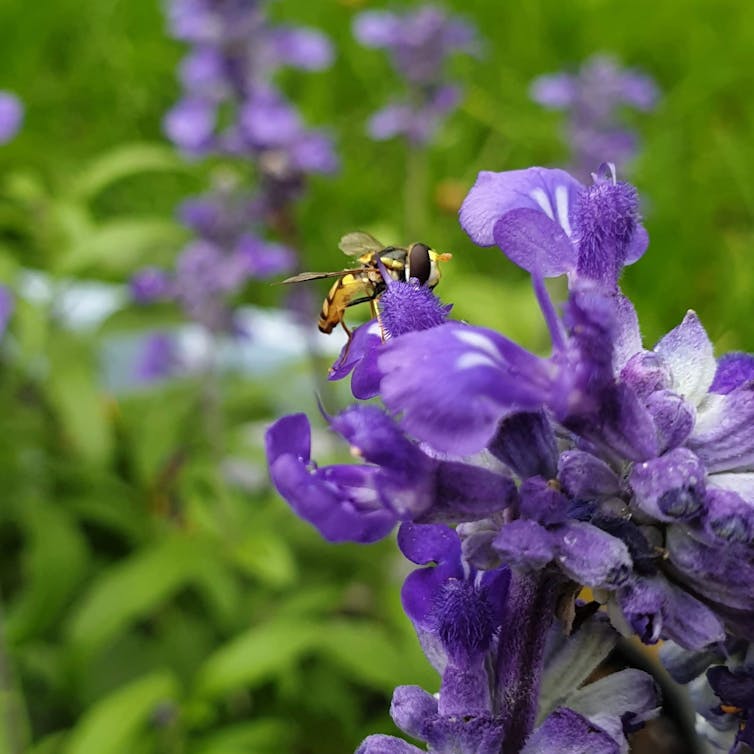 Hoverflies have similar colouring to honeybees.
Caitlyn Forster
Hoverflies have similar colouring to honeybees.
Caitlyn Forster
Bees out and about
Bees on flowers are usually more interested in the food they’re collecting than the people around them. However, if you’re concerned about encountering one on your morning walk or in the garden, there are simple ways to mitigate the risk.
Bees sting when they feel threatened. So when you see one, move slowly and keep your distance. If bees fly close to you, avoid sudden movements such as swatting them away.
And wear closed shoes where bees might fly close to the ground, such as around clover or fallen jacaranda flowers.
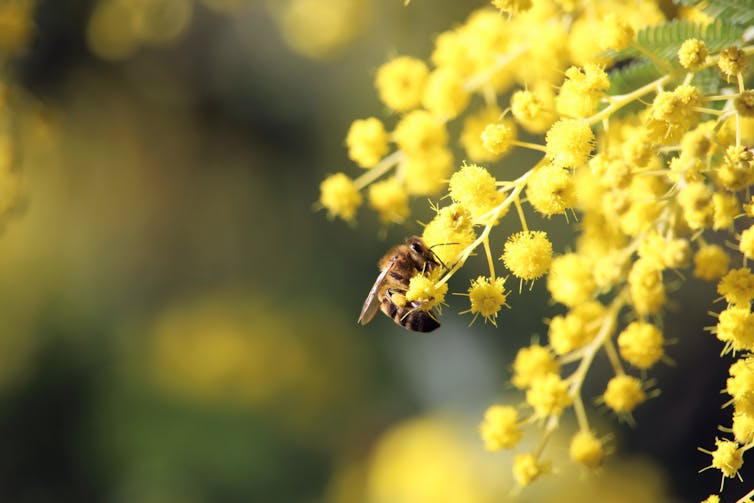 If you see a bee in the garden, avoid sudden movements.
Shutterstock
If you see a bee in the garden, avoid sudden movements.
Shutterstock
What if I see a swarm?
In spring and into summer, healthy honeybee colonies may reproduce by dividing into two. One part of the colony stays at the hive and the other goes looking for a new home.
Worker bees and the queen bee leave the hive in a swarm and find a spot to stay temporarily while scout bees find a new home. That’s when you might see a swarm on a tree, vehicle or building.
Once scout bees find a new home, they return to the swarm and communicate the location via the “waggle dance”. Once a sufficient number of scouts agree on a new nest site, the swarm lifts into the air and flies to its new home.
Read more: Curious Kids: how do bees make honey?
Don’t panic if you encounter a stationary swarm of bees. The bees will sting only if threatened. But keep your distance.
Moving swarms can pose a higher sting risk, and should be avoided. If you encounter one, move a safe distance away, or indoors if possible. When moving away, avoid fast movements or swatting.
Swarms are usually present for a few hours or days before they move to a permanent location. If the bees are in a risky location (for example, near a footpath or other busy areas), call a beekeeper to safely remove them.
Stingless native bees swarm for two reasons: mating and fighting.
Mating swarms involve males congregating outside a hive to mate with the queen. Fighting swarms occur when a colony of stingless bees attempts to invade another colony. They do not usually pose a risk to humans.
Native bees capable of stinging are solitary, so don’t swarm. However, male solitary bees are known to group together on branches in the evening.
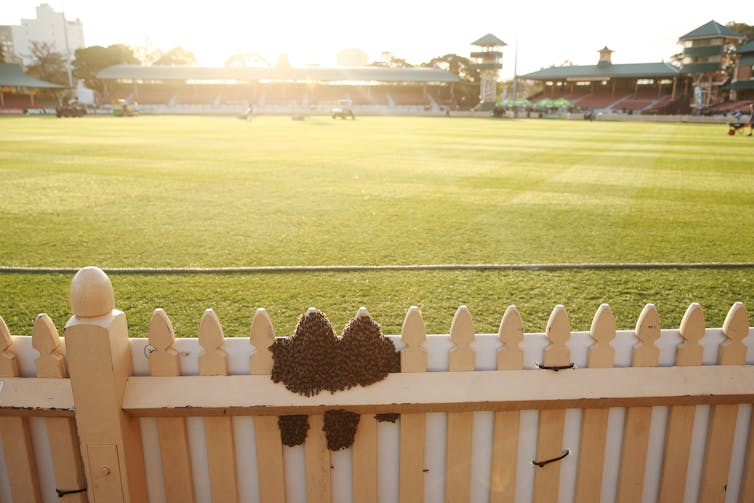 Bee swarms, such as this on a fence during a 2018 cricket match, usually move on in a few days.
Brendon Thorne
Bee swarms, such as this on a fence during a 2018 cricket match, usually move on in a few days.
Brendon Thorne
When a bee sting happens
Death and serious injury from bee stings is rare. But in Australia, bees are responsible for more hospital visits than snakes or spiders. European honeybees are also responsible for more allergic reactions than any other insect.
Only female bees can sting. Honeybees can only sting once, and die shortly after. This is because their stinger is barbed – once it stings something, the bee can’t pull the stinger out. Instead the stinger pulls free from the bee’s abdomen and the bee dies.
Other species can sting multiple times because their stingers are not barbed.
When a bee’s stinger enters your skin, it injects venom from a sac on its abdomen. When this happens, you’re likely to experience temporary swelling and redness.
For most people, reactions to bee venom are shortlived. To limit the amount of venom injected by the bee, quickly remove the sting using the edge of your fingernail or credit card.
In some cases, stings can lead to severe allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis. If you think you may have an allergy to bee stings, speak to your doctor.
And seek medical advice if you are stung in the face or neck, if significant swelling occurs or if you develop symptoms such as wheezing, light-headedness or dizziness.
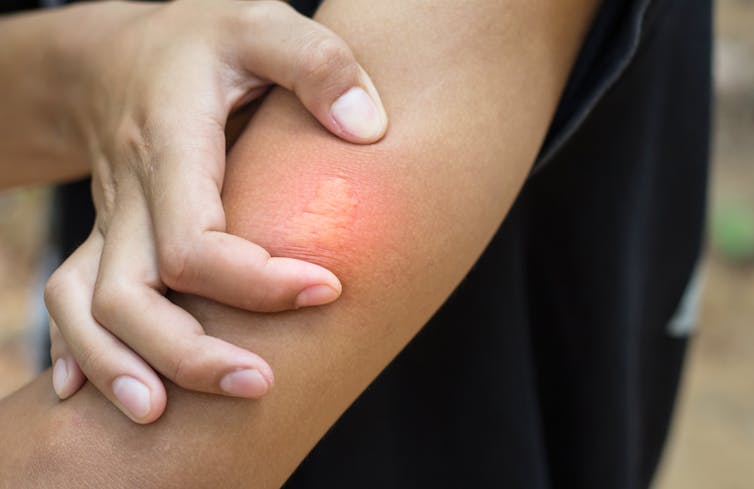 Many people develop swelling and redness after a bee sting.
Shutterstock
Many people develop swelling and redness after a bee sting.
Shutterstock
Learning to like bees
Bees and other insects play an important role in our food production, by moving pollen from one plant to another. They do a similar job in your garden, helping flowers and fruits to flourish.
But worldwide, bees and other pollinators face many threats, including climate change, misuse of pesticides and habitat loss. We must do what we can to keep pollinator populations healthy.
So if you’re out and about and see a bee, or even a swarm, try not to panic. The bees are probably focused on the job at hand, and not interested in you at all.
Read more: 'Jewel of nature': scientists fight to save a glittering green bee after the summer fires
Authors: Caitlyn Forster, PhD Candidate, School of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Sydney




