Sweden eschewed lockdowns. It's too early to be certain it was wrong
- Written by Andreas Ortmann, Professor, UNSW
Sweden has become something of a cautionary tale for what happens when you attempt to tackle coronavirus without lockdowns.
In The Conversation last week The Grattan Institute’s Stephen Duckett and Will Mackey said its freer approach caused almost as much economic damage as a lockdown would have, and many more deaths.
It’s a theme taken up in the New York Times and in an upcoming book.
Sweden’s death rate is indeed high compared to others at this stage.
At the time of writing worldometer suggests Sweden is one of the worst nations in the world in terms of deaths per million population, being beaten among the populous nations only by Belgium, Britain, Spain, Italy, and Peru.
So far Sweden’s done badly in terms of deaths
At 568 deaths per million it has done worse than the United States (480) and much worse than nations such as Denmark (106), Australia (9) South Korea (6) and New Zealand (4).
And on one reading its economic performance doesn’t seem much better than Denmark’s.
Denmark imposed strict restrictions from early March, closing the border to all foreign nationals, limiting social gatherings to ten, shutting schools, universities and non-essential work, and encouraging the entire population to stay home and minimise social contact.
Read more: No, Australia should not follow Sweden's approach to coronavirus
Neighbouring Sweden allowed bars and restaurants to remain open with capacity constraints and table service. Preschools and primary schools were kept open but senior schools closed, and its borders remained open to people from Europe. At the same time it banned visitors from aged care facilities and encouraged old people and those with pre-existing health conditions to avoid social contact.
The University of Copenhagen study cited by those who argue Sweden got it wrong finds that in Sweden aggregate spending dropped 25% whereas in neighbouring Denmark it dropped 29%.
The authors conclude
even when there are no major restrictions on economic activity, as in Sweden, a pandemic induces a sizeable contraction of spending; the additional drop in spending caused by a shutdown, as in Denmark, is relatively small
But it might not stay that way
The University of Copenhagen study was close to a snapshot, presenting data for the four weeks between March 11 to April 5.
Shortly after the snapshot ended, after April 5, Sweden’s daily death count began falling. Its daily deaths are now close to zero.
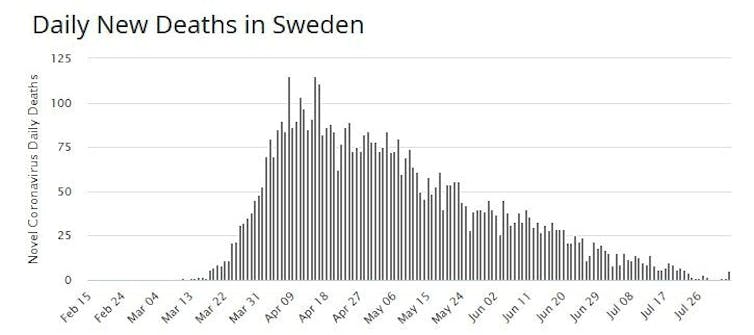 Worldometer
Denmark’s death count has also declined, but less smoothly.
Worldometer
Denmark’s death count has also declined, but less smoothly.
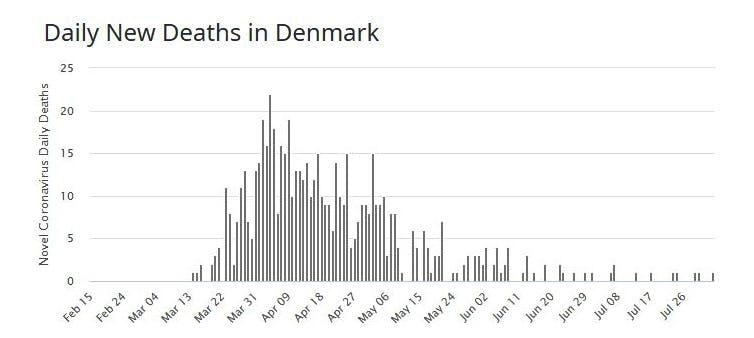 Worldometer
Death counts in Australia and many other countries that imposed hard lockdowns are turning up as they get hit with second waves and second lockdowns.
Worldometer
Death counts in Australia and many other countries that imposed hard lockdowns are turning up as they get hit with second waves and second lockdowns.
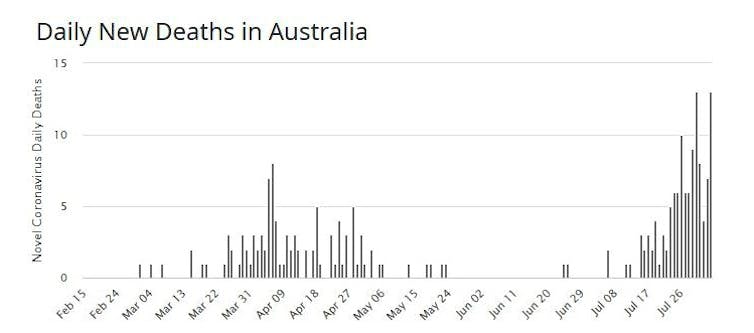 Worldometer
Anders Tegnell, Sweden’s chief epidemiologist, says in many ways the voluntary measures put in place in Sweden were just as effective as the complete lockdowns in other countries, and might be more sustainable.
On its performance to date, Sweden has the world’s eighth highest death rate.
But if present trends continue, the ranking will fall. It is possible that by the time a proper accounting is done it won’t even make the top 20.
We will know soon how Sweden did economically in the second quarter of the year. Bank forecasts have its economy down only 7% to 8% in that quarter compared to 12% for the European Union as a whole.
It’s too early for a full accounting
A full accounting of how Sweden’s approach has fared compared to other country’s will take time, and will involve trading off health, economic, educational and other outcomes.
Confidence in its Public Health Agency remains high at 65%, suggesting Swedes are not unhappy with the tradeoffs made. And they are prepared to follow directions, perhaps more than Australians and residents of the United States and the much-touted Germany.
Sweden’s Civil Contingencies Agency says 87% of the population is complying with the social distancing restrictions that are in place, up from 82% a month ago.
Worldometer
Anders Tegnell, Sweden’s chief epidemiologist, says in many ways the voluntary measures put in place in Sweden were just as effective as the complete lockdowns in other countries, and might be more sustainable.
On its performance to date, Sweden has the world’s eighth highest death rate.
But if present trends continue, the ranking will fall. It is possible that by the time a proper accounting is done it won’t even make the top 20.
We will know soon how Sweden did economically in the second quarter of the year. Bank forecasts have its economy down only 7% to 8% in that quarter compared to 12% for the European Union as a whole.
It’s too early for a full accounting
A full accounting of how Sweden’s approach has fared compared to other country’s will take time, and will involve trading off health, economic, educational and other outcomes.
Confidence in its Public Health Agency remains high at 65%, suggesting Swedes are not unhappy with the tradeoffs made. And they are prepared to follow directions, perhaps more than Australians and residents of the United States and the much-touted Germany.
Sweden’s Civil Contingencies Agency says 87% of the population is complying with the social distancing restrictions that are in place, up from 82% a month ago.
Authors: Andreas Ortmann, Professor, UNSW





