First home buyer schemes aren't enough to meet young adults' housing aspirations
- Written by Sharon Parkinson, Senior Research Fellow, Centre for Urban Transitions, Swinburne University of Technology
Young adults not only struggle to buy a home, many struggle to secure any kind of independent housing. This contributes to a cycle of living in precarious and informal housing and to a growing gap between their current situation and their short and longer-term housing aspirations.
A report released today by the Australian Housing and Urban Research Institute (AHURI) adds nuance to debates about generational change and housing by examining how housing aspirations differ among emerging adults (18-24 years) and in early adulthood (25-34 years). For example, emerging adults are more likely than the older cohort to prefer living in an apartment.
By early adulthood, the housing aspirations gap is greatest for individuals in the private rental sector, particularly those on higher incomes, and narrowest for home owners. Home buyers on low to moderate incomes are most happy with their housing.
Read more: Moving on from home ownership for 'Generation Rent'
While long-held values around the ideal of home ownership prevail, these are not as persistent as for past generations. The ideal differs according to age, education and the quality and security of current living arrangements. But having somewhere safe and secure to call home was the top priority across all young adults.
Aspirations change with stage of life
An extended phase of dependence to semi-dependence shapes the housing aspirations of young adults. This involves either remaining in the family home or sharing with others.
In 2015-16, the ABS Survey of Income and Housing revealed that only one in six (17%) young adults (18-24 years) lived independently. Two-thirds (66%) lived with parents. Around a third of young adults (25-34 years) are also opting to remain or move back with parents or live in shared housing.
While these living arrangements reflect concerns about housing affordability, they are also used as a strategy to pursue other aspirations, such as education.
What do young adults want in their housing?
The AHURI research includes a nationally representative survey of more than 2,400 Australians aged 18-34 years. It was supported by focus groups and in-depth interviews, including with Indigenous Australians, in Western Australia, New South Wales and Victoria.
Home ownership was the ideal tenure for 60% of emerging adults (18-24). By early adulthood (25-34) the proportion had climbed to 70%. The ideal of home ownership was lower (61%) for those still living in the family home by early adulthood compared with higher-income couples living independently (80%).
By early adulthood, educational status becomes a key marker of whether home ownership is considered possible. Nearly two-thirds (61%) of households with a tertiary-educated member believed they could buy a house within five years. This compares with just over a third of those with an education to year 12 (36%) and less than a quarter (23%) of those with an education to year 11 or below.
The preference for apartment living falls with age. About a third (34%) of emerging adults reported this as their ideal, compared with 21% of early adults.
Young adults also want more space. The largest share of both emerging (32%) and early adults (43%) indicated that a four-bedroom house is ideal. This compares to just 20% of those over 55 years of age who wanted four or more bedrooms.
Read more: What sort of housing do older Australians want and where do they want to live?
How large is the housing aspirations gap?
For emerging adults (18-24), living in a group household typically met short-term (82%) but not longer-term (25%) aspirations. Similarly, living with parents mostly met short-term (76%) but not longer-term (30%) aspirations.
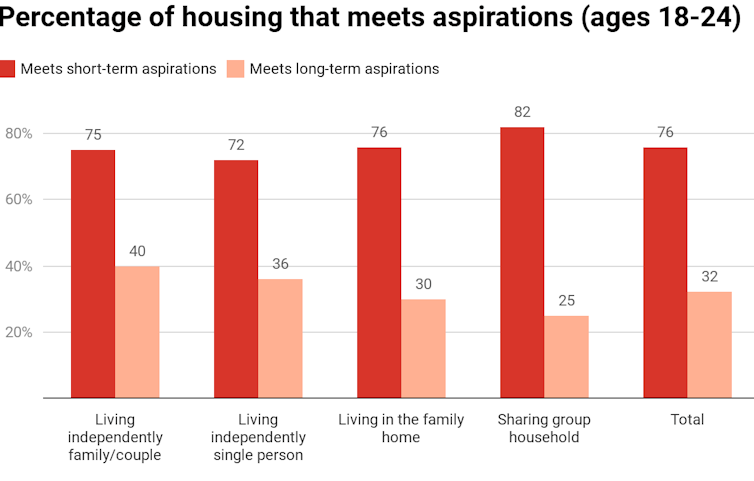 Australian Housing Aspirations Survey 2018, Author provided
By early adulthood (25-34) the housing aspirations gap is greatest for individuals in the private rental sector, particularly those on higher incomes. For higher-income groups, their current private rental housing met the short-term aspirations of just over three-quarters (76%) but only 20% for longer-term aspirations.
The aspirations gap is narrowest for home owners. Home buyers on low to moderate incomes were most happy with their housing in the short-term (92%) and longer-term (60%).
Australian Housing Aspirations Survey 2018, Author provided
By early adulthood (25-34) the housing aspirations gap is greatest for individuals in the private rental sector, particularly those on higher incomes. For higher-income groups, their current private rental housing met the short-term aspirations of just over three-quarters (76%) but only 20% for longer-term aspirations.
The aspirations gap is narrowest for home owners. Home buyers on low to moderate incomes were most happy with their housing in the short-term (92%) and longer-term (60%).
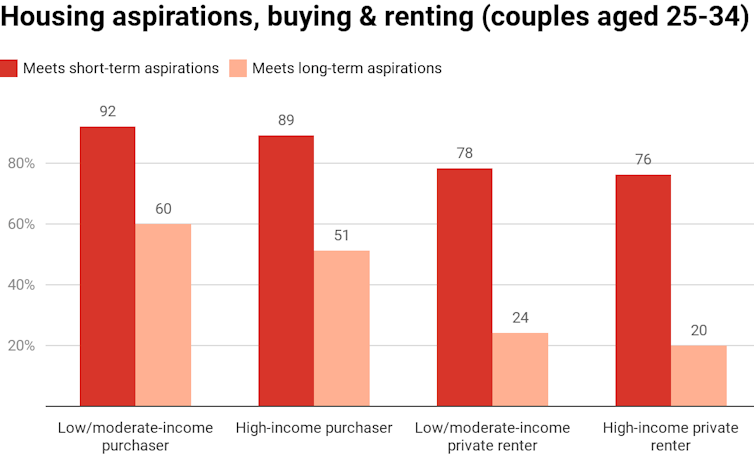 Housing Aspirations Survey 2018, Author provided
What can be done to close the aspirations gap?
Very few people are actively planning for their housing futures. Affordability and the deposit gap, insufficient income, employment insecurity and “waiting for the market to settle down” all impact on achieving longer-term aspirations. In the short-term, not being in a preferred location, high mobility and insecurity matter most.
Housing policy needs to become more realistic about the housing futures of young Australians. Achieving both short- and longer-term aspirations requires new policy frameworks that can enable young people to move towards attaining “secure independence”.
Public debate about the housing aspirations of young adults gained prominence during the federal election with promises of a targeted scheme to help first home buyers. Proposed first home owner deposit schemes are an important step in meeting aspirations, particularly among private renters with higher and secure incomes.
Read more:
Small, but well-formed. The new home deposit scheme will help, and it's unlikely to push up prices
But before young people even contemplate home ownership they need greater support in making key life transitions, such as from education to work, via more continuous and integrated packages of housing assistance.
We also need continued reforms to ensure a fairer and more secure private rental sector with short and longer-term leasing options close to employment and training, and with stable rents.
There needs to be diversity and real choice in dwelling types, size and locations and scaling up of more sustainable and niche models of co-housing.
Read more:
We need more flexible housing for 21st-century lives
As for young people locked out of home ownership in the long-term, they need a way to build an investment nest egg and to access quality social and public rental housing.
Housing Aspirations Survey 2018, Author provided
What can be done to close the aspirations gap?
Very few people are actively planning for their housing futures. Affordability and the deposit gap, insufficient income, employment insecurity and “waiting for the market to settle down” all impact on achieving longer-term aspirations. In the short-term, not being in a preferred location, high mobility and insecurity matter most.
Housing policy needs to become more realistic about the housing futures of young Australians. Achieving both short- and longer-term aspirations requires new policy frameworks that can enable young people to move towards attaining “secure independence”.
Public debate about the housing aspirations of young adults gained prominence during the federal election with promises of a targeted scheme to help first home buyers. Proposed first home owner deposit schemes are an important step in meeting aspirations, particularly among private renters with higher and secure incomes.
Read more:
Small, but well-formed. The new home deposit scheme will help, and it's unlikely to push up prices
But before young people even contemplate home ownership they need greater support in making key life transitions, such as from education to work, via more continuous and integrated packages of housing assistance.
We also need continued reforms to ensure a fairer and more secure private rental sector with short and longer-term leasing options close to employment and training, and with stable rents.
There needs to be diversity and real choice in dwelling types, size and locations and scaling up of more sustainable and niche models of co-housing.
Read more:
We need more flexible housing for 21st-century lives
As for young people locked out of home ownership in the long-term, they need a way to build an investment nest egg and to access quality social and public rental housing.
Authors: Sharon Parkinson, Senior Research Fellow, Centre for Urban Transitions, Swinburne University of Technology





