Here's what the budget did to get Australians into homes (hint: not much)
- Written by Yogi Vidyattama, Associate Professor, National Centre for Social and Economic Modelling, University of Canberra
Among the bolder claims in last month’s budget was that “under the Coalition, home ownership will always be supported”.
Since the Howard government took office in 1996, the proportion of Australian households owning the home they live in has fallen from 70% to 66%.
The proportion having paid off their mortgage has fallen from 40% to 30%.
The proportion renting privately has climbed from 20% to 27%.
In the lead up to the budget, home prices began climbing again, soaring 8.5% so far this year in Melbourne and 11% in Sydney.
The response was a series of measures designed to look as if they would help people buy their own homes.
Shuffling the queue
On examination, each measure is less than it could be, although each helps some people more than others.
Usually first home buyers with less than a 20% deposit need to pay lenders’ mortgage insurance.
Under two of the schemes they can effectively get this cost met by the government.
Extending the First Home Loan Deposit Scheme will allow 10,000 more first home buyers to buy newly-constructed dwellings with a 5% deposit.
Read more: Paying off a home loan used to be easier than it looked. It's now harder. Here's why
A separate new Family Home Guarantee will allow 10,000 single parents to buy a new or existing home with just a 2% deposit.
Both are only open to single applicants with annual taxable incomes of $125,000 or less. Couples have to earn $200,000 or less.
The measures have similar problems to the First Home Owners Grant schemes in place intermittently since 1964.
They add to demand for housing but not its supply.
Not quite helping those most in need
This means that while the schemes assist (doubtless worthy) people buy homes, they do it at the expense of others who miss out.
 Homebuilder, used for knockdowns and rebuilds.
Twin Sails/Shutterstock
Homebuilder, used for knockdowns and rebuilds.
Twin Sails/Shutterstock
They shuffle rather than shrink the queue.
A separate measure since closed, HomeBuilder, awarded grants for the construction of homes, but it was also available for knockdowns, rebuilds and extensions rather than being directly targeted at increasing supply.
Only three economists responding to the Economic Society of Australia’s post-budget survey referred to the housing measures and none were supportive.
Our calculations using NATSEM’s STINMOD+ model suggest that even if these schemes were not limited to 10,000 applicants, there may not have been many households able to take them up.
Only 5% of private renters, and 7% of single parents, have enough savings to enter the housing market, even with the promised mortgage insurance guarantee.
Young urban professionals
Of these, more than 85% would then be paying more in servicing costs than they currently pay in rent, even at today’s historically low interest rates.
They might not regard this as an improvement in affordability.
In any case, it wouldn’t be the poorest households being helped.
Our calculations suggest the poorest fifth of households would be unlikely to have enough savings to use the deposit insurance schemes.
Read more: HomeBuilder only makes sense as a nod to Morrison's home-owning base
Those most likely to use them are on higher incomes but still renting. They include young urban professionals in the eastern and northern suburbs of Sydney.
The blue areas on this map show the regions with the most households who might benefit.
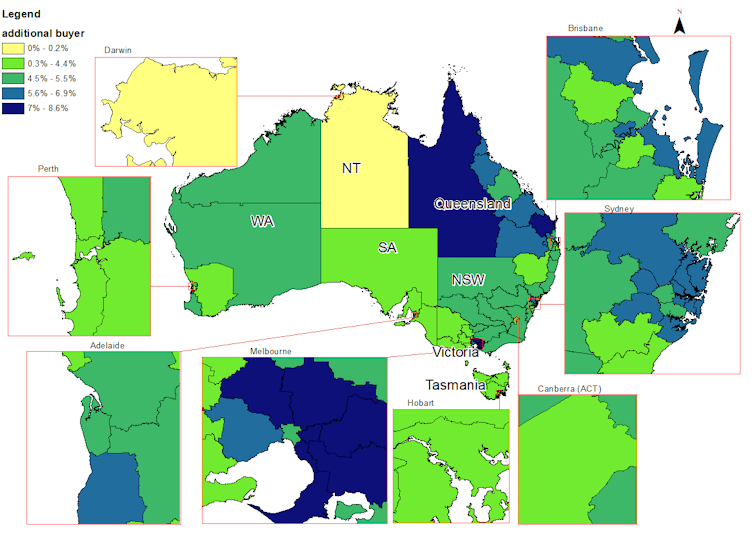 NATSEM
The schemes would be more helpful for potential homebuyers in regional areas than in cities, but they are less likely to have the income and savings needed to take advantage of them.
The schemes also have price caps below the median house price in most capital cities, making it hard for people such as parents who need extra bedrooms to take advantage of them.
The downsizer initiative will help
A more promising initiative in the budget is lowering the minimum age at which downsizers can access the downsizer contributions scheme from 65 to 60.
This scheme allows older Australians to downsize and put the proceeds into lightly-taxed superannuation.
This will free up family homes for the younger generations, although it will not help those on low incomes buy them.
NATSEM
The schemes would be more helpful for potential homebuyers in regional areas than in cities, but they are less likely to have the income and savings needed to take advantage of them.
The schemes also have price caps below the median house price in most capital cities, making it hard for people such as parents who need extra bedrooms to take advantage of them.
The downsizer initiative will help
A more promising initiative in the budget is lowering the minimum age at which downsizers can access the downsizer contributions scheme from 65 to 60.
This scheme allows older Australians to downsize and put the proceeds into lightly-taxed superannuation.
This will free up family homes for the younger generations, although it will not help those on low incomes buy them.
Authors: Yogi Vidyattama, Associate Professor, National Centre for Social and Economic Modelling, University of Canberra





